




Scan your phone once
MingFan Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. specializes in the research, development, and manufacturing of core surface treatment equipment, including electrostatic spraying systems and conveyor ovens.
Driven by technological foresight and innovation, we persist in independent R&D. While continuously launching efficient, energy-saving, and eco-friendly new products, we actively explore and independently develop supporting consumables designed to significantly reduce customer operating costs.
Leveraging our diverse product portfolio, we are committed to providing customers across industries with high-performance, comprehensive surface treatment solutions. From core equipment to critical consumables, we have built a diversified product ecosystem. Through the continuous accumulation of expertise and technical experience, we establish long-term strategic partnerships with industry leaders, jointly promoting sustainable development in the surface treatment field.
Differences Between Electrostatic Powder Coating and Traditional Paint Spraying
Spraying Mechanism:
Paint Spraying: Utilizes compressed air to atomize liquid paint into fine mist particles that adhere to the substrate surface.
Powder Coating: Relies on compressed air to fluidize the powder, which is then dispersed into fine particles under high-voltage electrostatic force and adsorbed onto the substrate via an electric field.
Equipment & Material Composition:
Paint Spraying: Can be applied using conventional spray guns.
Powder Coating: Correctly termed electrostatic powder spraying, requires specialized equipment:
Powder feed hopper (fluidized by compressed air)
High-voltage electrostatic generator
Electrostatic spray gun
Material: The coating material is powder, commonly called "plastic powder" (full name: plastic coating powder). Key categories include:
Outdoor-grade powder (e.g., polyester-based)
Indoor-grade powder (e.g., epoxy-based)
→ Fundamental distinction: Powder coatings and liquid paints are chemically distinct materials.
Characteristics of Liquid Paint Spraying Process:
Extensive Product Range & Selection Flexibility
China classifies paints into 17 major categories, with thousands of commercially available formulations and continuous new developments. Users can select optimal paints based on performance requirements, application scenarios, and environmental conditions.
Superior Aesthetics & Surface Smoothness
Delivers exceptional visual appeal with high gloss and flawless leveling. Achieves ultra-thin coatings (e.g., automotive finishes) unattainable with powder coating.
Lower Initial Investment & Operational Simplicity
Air Spraying (most common method): Ideal for small/medium-scale projects.
Equipment: Spray gun, air compressor, moisture separator, and air hoses.
Cost Advantage: Minimal upfront investment vs. powder coating systems (saving ¥100,000s). Enables rapid ROI and low production costs.
Higher Skill Requirements
Operators must master:
Paint properties, applications, and compatibility
Color theory (custom tinting from base pigments)
Multi-layer techniques (primer → filler → topcoat) to prevent defects.
Longer Production Cycles & Higher Overall Costs
Typical 6-Step Process:
① Preparation (viscosity adjustment, filtration, tinting)
② Primer application
③ Filler application
④ Mid-coat application
⑤ Sanding
⑥ Topcoat application
Cost Drivers:
Material consumption (primers/fillers/thinners/topcoats)
Drying/curing time (hours/days between layers)
Energy-intensive forced drying
Higher labor input
Environmental & Health Hazards
VOC Emissions: Solvents evaporate during application/curing.
Overspray Mist: Requires respirators and advanced ventilation.
Non-compliant with ISO 14001 (vs. powder coatings).
Higher Fire Risk vs. Powder Coating
Key Risk Factors:
Flammable Solvents: Ignite instantly upon spark exposure (flash point < powder coatings).
Rapid Flame Spread: Accelerated by volatile organics.
Inferior Ventilation: Standard in paint shops vs. powder systems.
Critical Note: Powder explosions (though rarer) are significantly more destructive than paint fires.
Comparative Analysis of Powder Coating vs. Liquid Paint Spraying Processes
Powder Coating Process Characteristics:
Solvent-Free & Eco-Friendly
Powder coatings contain no additives and are 100% solid-content materials. Their production, transport, storage, and application eliminate solvent-induced pollution, improving operator working conditions and ensuring occupational health.
Streamlined Process
Powder coating involves only three steps: spraying → curing → cooling, achieving single-coat film formation. This significantly simplifies workflows, shortens production cycles (products completed within one day), and enables automation when integrated with robotic spray systems and powder recovery units—enhancing energy/resource efficiency and productivity.
High Material Utilization (>95%)
Oversprayed powder is collected and recycled into the feed system, minimizing waste.
Superior Film Performance
Utilizes resins insoluble at room temperature or high-molecular-weight polymers unachievable in liquid form, yielding dense, durable coatings. No solvent emission during application prevents pinholes, ensuring uniform film integrity.
Thick-Film Application in Single Pass
Achieves 50–300μm coatings in one application without runs, sags, solvent pinholes, or edge coverage issues. Comparatively, liquid paint requires multiple coats (5–20μm per layer) for equivalent thickness or quality.
Color Change Limitations
Powder colors are factory-pre-mixed (no on-site tinting).
Switching colors requires full system purge (guns, hoppers, booths, hoses, recovery units) to prevent cross-contamination.
Deep-to-light color transitions are particularly time-intensive.
Minimum Film Thickness Constraint
Electrostatic application inherently produces coatings ≥40μm (typically 50μm+), even with premium powders and optimal conditions. Sub-40μm films remain technically challenging.
Inferior Leveling vs. Liquid Paint
Higher melt viscosity during thermal curing results in slight orange peel texture, yielding less smooth surfaces than solvent-based paints.
Application Limitations
Thermal Sensitivity: Curing temperatures >160°C exclude heat-sensitive substrates (e.g., plastics).
Conductivity Requirement: Electrostatic application mandates conductive substrates. Non-metallic parts require conductive pretreatment AND must withstand >160°C curing.
Previous:First
Next :Last
MINGFAN Import and Export Trade (Dezhou) Co., Ltd.
+86-18315884617Follow Us
Copyright © 2026 Dezhou Mingfan Coating Equipment Co., Ltd.All rights reserved.
If you have any queries, get in touch today! Don't hesitate. We try to take the extra step for our customer satisfaction.

| Product Picture | Product Name |
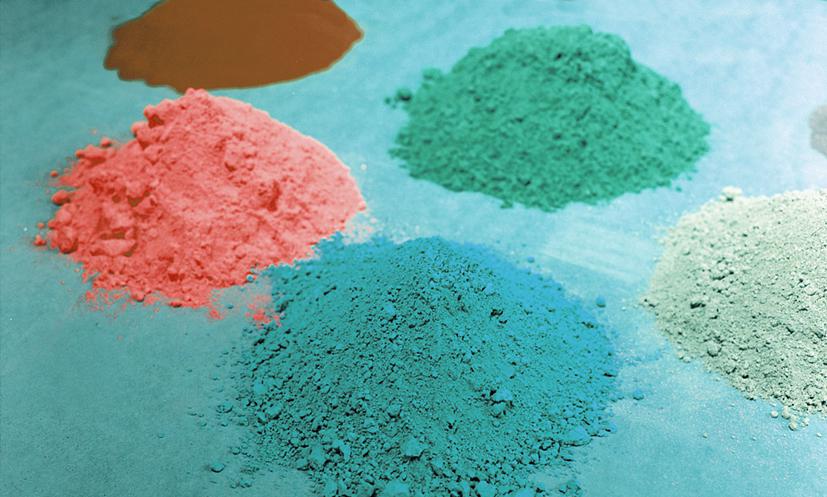 |
Electrostatic Spray Powder Coatings |